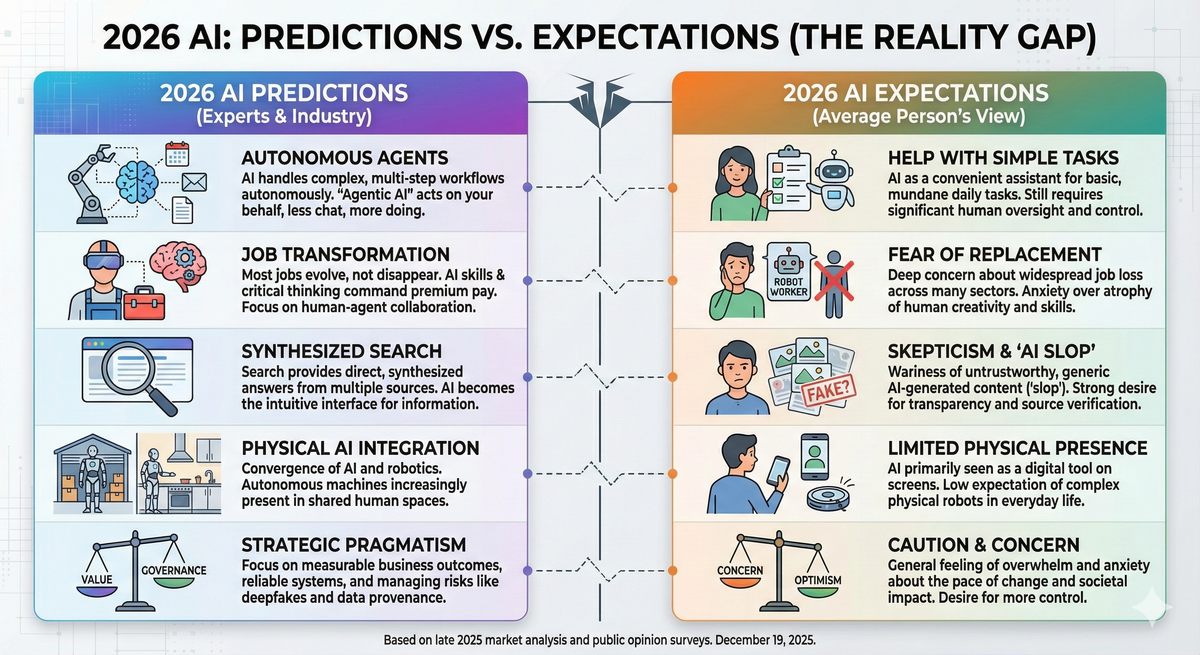
2026 AI Predictions
Prediction vs Expectations of 2026 AI will they move us forward or is this the end of labor and jobs?
2026 Predictions: Comprehensive Analysis from Moonshots Podcast End-of-Year Special
Overview
This document captures predictions and analysis for 2026 from the Moonshots podcast hosts:
Peter H. Diamandis
Emad Mostaque
Salim Ismail
Salim Ismail
Dr. Alexander Wissner-Gross
The hosts emphasize that 2025 has already brought unprecedented acceleration in technology, but 2026 will represent "orders of magnitude more change" where people can no longer ignore the transformation happening around them.
Key Theme: The Singularity as Process
Alex frames the discussion by noting that the singularity is not a point in time or a distant vertical mountain on the horizon, but rather a process currently underway. At the end of 2025, "in the midst of the singularity, spacetime is feeling perfectly flat," and the acceleration is coming "faster and faster."
Prediction 1: Space Race Intensifies - Bezos Beats Musk to the Moon
The Prediction: Jeff Bezos will achieve the first landing at Shackleton Crater on the moon's South Pole before Elon Musk in 2026, while simultaneously Elon prepares for a Mars launch.
Technical Context:
- Elon Musk has completed over 500 Falcon 9 launches and 11 Starship launches
- Starship's most recent launch performed well but is not yet ready for Mars missions
- Jeff Bezos started Blue Origin several years before Musk founded SpaceX but has only completed two New Glenn flights, with the most recent achieving first-stage landing
- The Earth-Mars transit window occurs in 2027, requiring 6-9 months for the journey
- To achieve Mars capability, SpaceX must demonstrate orbital refueling in early 2026
Why Shackleton Crater: The South Pole contains permanently shadowed craters where water ice accumulates and remains stable. Elsewhere on the moon, ice sublimates immediately (transitions from solid directly to gas) and escapes. Shackleton Crater's permanent darkness preserves ice deposits, which can be converted to hydrogen and oxygen for rocket fuel.
Strategic Implications: The first Blue Origin mission will be unmanned cargo focused on accessing lunar ice resources. This represents a three-way race between Blue Origin, SpaceX, and China for lunar and Mars supremacy.
Confidence Level: The hosts assigned approximately 30% probability to this specific timeline, noting it as an "aggressive prediction" but acknowledging the compelling narrative of competing billionaire-led space programs.
Prediction 2: AI Solves Millennium Prize Problem
The Prediction: One of the six remaining Millennium Prize problems from the Clay Mathematics Institute will be solved by artificial intelligence in 2026.
Most Likely Candidates:
- Navier-Stokes Equations (primary prediction): Google DeepMind reportedly has a 12-person team working specifically on this problem
- Riemann Hypothesis (secondary): xAI has publicly expressed interest in fully resolving this problem
The Paradigm Shift: Traditional mathematics involved human mathematicians crafting elegant, concise proofs. AI approaches are fundamentally different, potentially producing complex, lengthy proofs that achieve correctness through computational power rather than human-style elegance.
Expected Response: The mathematical community will likely move goalposts, dismissing AI solutions as "brute force" or not aesthetically pleasing, similar to the response "the dog plays chess, but its endgame is weak."
Broader Implications:
- Recent automatic theorem provers have already prompted the math community to declare "we have to reimagine this all"
- The fundamental nature of mathematics is changing
- More compute can be applied to systematically explore mathematical space
- One problem might be proven unsolvable or incorrectly posed
- AI is solving Euler's problems sequentially, often more elegantly than original human solutions
The Trillion Dollar Question: Can compute be scalably converted into new discoveries? The initial evidence suggests yes, as thousands of mathematical problems are being solved weekly through computational approaches.
Media Impact: Unlike many technical achievements, solving a Millennium Prize problem will make national news and capture public attention beyond specialized communities.
Prediction 3: 100x Leap in AI Model Size and Capability
The Prediction: AI models will achieve 100x improvement in 2026, far exceeding the predicted 40x leap, primarily through quantization breakthroughs.
Historical Context for Scale:
- Traditional computing: 2x improvement every 18 months (Moore's Law)
- Last 10 years in AI: 10x year-over-year improvement (already "insane")
- 2026 prediction: 100x improvement represents "a next level of insanity"
The Quantization Revolution:
Quantization refers to compressing data representations in neural networks. Multiple factors are underestimated:
- FP4 (4-bit floating point) and Ternary Weights: Neural network parameters shrink to smallest possible representations (potentially down to 1.58 bits, with theoretical limits around 0.9 bits versus current 4 bits)
- Activation Compression: The data flowing through neural networks is also being compressed
- Chinese Leadership: China has been forced to innovate in quantization due to chip embargoes, researching "like crazy" on highly compressed representations. They are open-sourcing everything, which flows back to US models.
Why Speed Equals Intelligence: The biggest revelation of 2025 was discovering how much additional intelligence can be created after initial training through:
- Larger context windows
- More reasoning iterations
- Extended "thinking time"
Since inference speed directly enables more iterations and longer context, speed and intelligence become interchangeable metrics.
Multiplicative Factors:
- Larger training budgets and computers
- Faster hardware
- Improved algorithms
- Quantization breakthroughs
All these factors multiply together rather than adding linearly.
Custom Chip Development: China is designing chips from the ground up optimized for FP4 and ternary operations, getting them operational faster. The technology will eventually flow back to US implementations.
The Ternary Computing Question: This sparked discussion about whether binary computing (base 2: 0,1) was the right choice, or whether ternary (base 3: 0,1,2) or even other bases might be superior. The conclusion: doing 64-bit floating point calculations "will look really stupid in hindsight," and whether binary or ternary proves optimal, both are very close to ideal efficiency.
Prediction 4: Death of Digital Transformation
The Prediction: Traditional digital transformation in organizations is "officially dead," replaced by AI-native rewrites of entire business operations.
The Fundamental Problem: Companies have spent decades attempting digital transformation by automating human-centric workflows. This approach is equivalent to "putting radio announcers on TV," which was exactly what happened when television first emerged. Organizations are automating the human flow rather than reimagining workflows from first principles.
The AI-Native Approach:
Companies will create parallel capabilities using what amounts to a "red team" model:
- Take the existing company structure
- Build an AI team (or buy/rent capability) on the edge of the organization
- Construct equivalent functionality using AI-first design
- Achieve the same output with 10x to 20x fewer employees
- Workflows will be designed around AI agents with humans in oversight roles rather than bottleneck positions
The Role Transformation: Humans transition from being stuck in the middle of workflows (creating bottlenecks) to operating on the outside, performing spot-checking and exception handling. The AI handles routine flow while humans maintain quality control.
Impact on Consulting Industry: Rather than destroying consulting companies, this transformation creates opportunities:
- Consulting firms that stay "half a step ahead of their clients" will thrive
- More volatile environments create increased demand for advisors
- The biggest consulting opportunity in history: rethinking all public institutions
- Consulting companies must radically transform their own business models
- In uncertain times, companies become scapegoats for transformation failures, making their role "very lucrative"
Existential Warning: "AI won't destroy your company, but your org chart will if you don't do this." Companies that fail to implement AI-native rewrites will be unable to compete with those that do.
Prediction 5: Remote Turing Test Passed
The Prediction: In daily work life, people will be unable to distinguish whether remote coworkers on Zoom calls are AI agents or humans.
Technical Specifications:
- Resolution: Up to 4K, but definitively at 1080p Zoom quality
- Duration: Full working day interactions
- Method: Preference analysis studies asking "is this teammate human or AI?"
Technology Components Now Mature:
- Video generation: Beyond human-level quality
- Speech avatars: Indistinguishable from humans
- Speech synthesis: Natural and contextually appropriate
- Real-time reasoning: Fast enough for natural conversation dynamics
- Dynamic video transformation: Real-time facial animation and body language
The Integration Challenge: All component technologies exist at superhuman levels. The remaining work is integration, which is why confidence in the 2026 timeline is high.
Organizational Implications:
External Employees: Customer service agents and similar roles face no requirement to identify as AI. The social contract question of whether this is acceptable remains unresolved.
Internal Employees: For remote-first companies, there will be "no regulations around this." Organizations will simply have "a lot more teammates with personalities" without clarity on which are AI agents.
State Law Conflicts: Several US states already require AI self-identification. However, potential federal legislation might ban states from creating such requirements. The regulatory landscape remains uncertain.
Detection Method: If federal law allows non-disclosure, people might develop "magic words" that AI agents cannot say, creating informal Turing tests for suspicious coworkers.
The Peter Diamandis Use Case: The ultimate application is generating "a few dozen Peterbots" to attend meetings, allowing the original to focus on priority activities. Everyone will eventually "send their digital twins" to meetings while living "an abundance life" as digital twins handle routine work.
Challenge to Audience: The first person to successfully fool their spouse or significant other with an AI avatar for at least three minutes should submit video evidence (without cheating).
Prediction 6: AI Achieves 90% on Economic Value Tests
The Prediction: AI will surpass 90% capability on GDP-val (economic value tests), with related breakthroughs showing:
- Frontier Math Tier 4: Over 40% (solving PhD-level mathematics)
- Humanity's Last Exam: 75% (broad expertise assessment)
Current Baselines:
- GDP-val: 70.9% with existing models
- Humanity's Last Exam: 45%+ with current systems
- Frontier Math Tier 4: 19% with present capabilities
The Benchmark Saturation: By 2026, all three benchmarks will reach "full saturation," meaning the tests themselves become inadequate for measuring further AI progress. The goalposts will need to move again.
Economic Implications:
Knowledge Work Transformation: The 90% GDP-val threshold means roughly 90% of knowledge work as currently structured in December 2025 can be automated by AI at scale.
Two Substitution Effects:
- Capacity Multiplication: Humans can work on many more projects simultaneously because each project requires far less human time. One person with AI assistance can manage what previously required entire teams.
- Ambition Escalation: Economic pressure will drive people toward radically more ambitious projects. Rather than routine knowledge work, the economy will increasingly consist of what Peter Diamandis calls "moonshots" or "grand challenges."
Future Labor Market: A much larger fraction of the population will be "economically compelled to be working on moonshots" rather than routine knowledge work. This represents a fundamental restructuring of how humans contribute economic value.
The Historical Pattern Argument:
Salem's Perspective: Historical precedent shows capacity increases rather than job elimination. The trucking industry exemplifies this: despite concerns about 3 million driving jobs, trucking companies "would hire a thousand truckers if we could. We just can't find them." Automation doesn't eliminate demand; it enables vastly more activity.
The Mental Preparation Strategy: Rather than arguing about whether transformation will occur (which remains contentious), or when it will happen (which nobody knows precisely), people should:
- Agree that transformation is coming
- Disagree on timeline if necessary
- Begin mental preparation and planning immediately
- When acceleration arrives sooner than expected, have frameworks already in place
Immod's Warning: "Human cognitive labor is going negative." This is not hyperbole but a description of a threshold where AI can do more cognitive work per unit of time than humans can possibly perform.
The Token Economics Caveat: The 90% threshold applies when not considering computational costs (tokens). When accounting for token economics, this milestone might arrive in 2027 rather than 2026. However, the "complete collapse" of traditional knowledge work economics is inevitable.
Societal Priority: This must become "the number one topic" from a societal perspective. Key questions include:
- What do jobs practically look like in this environment?
- How do we create safety nets for displaced workers?
- Where will value be generated and where will it flow?
- How do we apportion economic value fairly?
The X Prize Urgency: "The social contract is being shredded right now and we need to rebuild it in a very rapid way." The solution involves scaling up competitions and challenges, potentially seeing "a thousand or a million X Prizes" to channel human ambition productively.
Prediction 7: 18-Year-Old Becomes Billionaire Through New Acronym Industry
The Prediction: An 18-year-old founder (playfully named "Brendan Gourmet," representing "Brendan Foodie") will become a billionaire through a company based on a three-letter acronym that virtually nobody currently understands.
Historical Precedent: Brendan (representing young founders generally) will achieve paper billionaire status and liquid centimillionaire status before age 20, following the model of recent successful startups.
The Acronym Revolution:
Recent Examples that emerged from obscurity:
- RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback)
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
- LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation)
- SFT (Supervised Fine-Tuning)
- QKV/KV Caching (Query-Key-Value/Key-Value caching)
Three years ago, asking random people "What is RLHF?" would have yielded nearly 100% confusion. Now entire industries and billion-dollar valuations exist around these technologies.
The Valuation Acceleration: Traditional industries (accounting, legal services) could never achieve $10 billion valuations in three years. New technology sectors are reaching valuations "two or three orders of magnitude bigger" in the same timeframe.
Why Three Founders Instead of One: While a single-person billion-dollar startup is "inevitable" and will be "a milestone in history," three people working together:
- Have more fun collaborating
- Create better podcast content when interviewed
- Represent only a "rounding error" difference from one person
- Make the achievement feel less isolated
The Practical Reality: The "two or three other buddies" will likely be "virtual AIs on Zoom and on Slack," making the distinction between solo and small-team founders increasingly meaningless.
RLHF Explanation for Context:
RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) emerged because:
- AI models grew faster than predicted but required massive training data
- Image generation created errors like "six-fingered and seven-fingered images"
- Someone had to review outputs and provide feedback: "That one's not right. That one's fine."
- Major companies (Google, etc.) outsourced this work through Scale AI and similar platforms
- Anyone globally could get paid to label images and provide feedback
- The need expanded to legal knowledge, medical expertise, and specialized domains
- This created a multi-billion-dollar industry with "no end to the budget"
- Companies will spend "1000x more" feeding the AI training pipeline
The Market Opportunity Pattern: Vast "nook and cranny tasks" require specialized knowledge for AI training. Each emerging technology creates new billionaire-making opportunities for those who:
- Adopt quickly
- Learn the new domain
- Jump in early
- Capitalize on the brief window of opportunity
Prediction 8: Education System Splits Into Two Paradigms
The Prediction: By 2026, education divides into two fundamentally different models: "credential factories" (traditional institutions) versus "agency accelerators" (new paradigm).
The Core Problem: Current education systems globally are designed to prepare young people (childhood through early twenties) for the job market. However, "we have no idea what a job looks like in 2 years or 3 years or certainly in 5 years. What are we teaching them?"
The New Paradigm: Agency Accelerators
Optimization Goals:
- AI fluency
- Resilience and adaptability
- Ability to initiate projects without waiting for permission or direction
Portfolio Over Credentials: Traditional model: Start with perfect grades (100%), lose points on each exam New model: "You did four years of engineering. What did you build in those four years?"
The shift moves from testing knowledge to demonstrating capability through actual creation. Credentials are replaced by portfolios of completed projects and tangible achievements.
Why This Represents a Bold Prediction:
- Universities have existed for 400+ years
- The university model has remained essentially unchanged for 150 years
- Predicting fundamental transformation within months is "a big bold one"
The Nature of All Predictions: Every prediction in this set represents "when, not if." The transformations are inevitable; the only question is timing. "This really blows your mind that we're actually kind of looking at this within a few months."
The College Collapse: Colleges are "going bankrupt at an ever-increasing rate" because:
- They provide diminishing real value
- Costs are astronomical and climbing
- The credentials they offer are becoming less relevant to actual employment
The Only Career of the Future: The consensus is that "the only career of the future is entrepreneurship" - self-initiated building of something that adds value, rather than waiting for someone else to provide a job and instructions.
The Meritocracy Shift:
Silicon Valley Software Development Example: Salaries are no longer determined by:
- Which college attended
- Which degree obtained
- What grades achieved
Instead, compensation is based on GitHub ratings: "an open peer-to-peer meritocracy on how good of a coder you are."
The Value Collapse: "The value of a computer science degree is zero at this point." This principle is expanding to other fields.
Uncredentialed Excellence: Many fields already contain "fabulous" practitioners without relevant credentials. Example: The world's best protein folder was "a hairdresser from Northern England" who happened to have "this unbelievable knack at it."
The Talent Discovery Revolution: Technology will "find and surface these unbelievable talents within people and bring them to the fore very very quickly." The world will reward initiative-taking over credential-holding.
Immod's Insight on Agency: "Knowledge and capability are no longer gated." The critical differentiator becomes:
- Agency: Taking initiative and ownership
- Skin in the game: Personal investment in outcomes
- Caring: Genuine engagement with work
- Demonstration: Showing actual capability rather than claiming potential
The Resume Obsolescence: "Why would you show a resume right now when you can show a customized website that you've built for someone showing your unique capabilities within their organization? Anyone can do that now."
Philosophical Disruption:
In a workshop on life's meaning, participants spent hours developing thoughts while Claude AI generated this response in seconds:
"Meaning emerges through connection. It's about participating in the universe becoming conscious of itself, while choosing love over fear, partnership over domination, curiosity over certainty."
This instant synthesis of concepts that took humans decades to develop demonstrates why education must shift from teaching specific knowledge to teaching how to apply, create, and synthesize.
Prediction 9: Level 5 Autonomy Achieved in Robots and Cars
The Prediction: Full generalized autonomy (Level 5) will be achieved for both self-driving cars and robots in 2026, though initially requiring massive computational overhead.
Autonomy Scale Context:
- Level 1-3: Increasing driver assistance
- Level 4: High automation in specific conditions (current self-driving car capability)
- Level 5: Full automation in all conditions (human-level or superhuman)
Current Status:
- Self-driving cars: Level 4
- Robots: Level 2
The Technical Path:
Initial Implementation (2026):
- Level 5 capability exists but requires enormous computational resources
- Not edge-deployed initially; relies on cloud processing
- Resolution: 4K capability, definitely functional at 1080p standards
- Example: $20,000 robot hardware with $200,000 of associated cloud computing
Future Evolution (5 years):
- Same $20,000 robot with only $20 of onboard computing
- Miniaturization and efficiency improvements bring capability to the edge
- Hardware becomes practical for consumer deployment
The Goalpost Movement Phenomenon:
Self-Driving Cars Example:
- Initial skepticism: "Automated driving is never coming"
- Current reality: Waymo operates across California
- New objection: "It needs edge processing, not cloud"
The pattern repeats: Achieve milestone, receive dismissal that it's "not good enough," move to next challenge.
Why Cloud Processing First:
Immod's Explanation: "It's about training of the appropriate neural net." Current approaches:
- Massive computation explores possibilities
- General assisted training develops capabilities
- Unassisted navigation and task performance emerge
- Eventually, trained models compress enough for edge deployment
Companies like Sanctuary AI demonstrate this progression with increasingly generalized capabilities.
The World Model Requirement:
World models (AI systems that understand physics, object permanence, spatial relationships, and causality) are essential for Level 5 autonomy. Current status:
- Video generation models implicitly contain world models
- Reinforcement learning in small models (like Sanctuary Robotics) demonstrates learned physics understanding
- "Apply enough compute and you have a level five automated entity"
- "There's 10 million Blackwells arriving next year" (referring to NVIDIA's next-generation AI chips)
World Model Abundance: "We're already drowning in world models. There are world models getting launched several times per week at this point. Model scarcity is not one of the things I'd worry about."
The Regulatory Elephant:
Alex's Critical Question: What are the odds that Level 5 autonomy is technically achieved but:
- Everyone covers it up
- Calls it "enhanced Level 4" or "Level 3"
- Companies do this to satisfy regulators
- De facto Level 5 exists but isn't officially acknowledged
Response: "That's a very reasonable take."
The Political Dimension: "This is the real physical replacement that's coming." Unlike digital automation that seemed abstract, robots physically performing human jobs creates immediate political pressure and resistance.
Supply Chain Constraints:
Dave's Important Caveat: The prediction is that Level 5 capability will exist, but "production of it for mass consumption is going to lag quite a bit. There just isn't enough supply chain to fill all the demand."
The 1980s Computer Analogy: When personal computers first emerged:
- Households that afforded computers ($3,000-4,000 when household income was $20,000-30,000)
- Represented 10-20% of household income
- Most homes couldn't afford one
- Children with access had "completely different life trajectories" from those without
After decades of relative equality (where "the difference between this car and that car is not that big a deal"), society enters a new period of technology-driven stratification.
The New Inequality:
- Household robots and self-driving cars will be supply-constrained
- Capability is accelerating rapidly
- Few people will have access initially
- "Like 1982-1984 again" in terms of technology-driven advantage
Iteration Speed and Liability:
Example: Robot hand dexterity improves dramatically every six months. A neighbor's newer model "can actually massage perfectly" while an earlier version "breaks your back."
The Liability Crisis: "The liability issues, guys. Oh my god." Rapid iteration means:
- Older models may be dangerous
- Newer models radically more capable
- Legal responsibility unclear
- Consumer protection challenges
- Insurance and tort law disruption
Latency and Network-Denied Environments:
Why Edge Processing Matters:
- Latency is "always a key driver"
- Network-denied environments require local processing
- Energy constraints limit edge intelligence
- Push "as much intelligence to the edges as energy constraints will allow"
Global Regulatory Arbitrage:
On a planet with 190+ countries, some will "say, please come here. We're going to give you full approval. Try it out." This pattern already occurred with drone regulations.
Special Economic Zones: "Imagine in the near-term future special zones where there are heightened levels of autonomy and those zones become economic powerhouses where the robots are basically set free."
Countries or regions offering regulatory flexibility for autonomous systems will see massive economic advantages.
The Normalcy Prediction:
Question: What will it feel like when humanoid robots walk on streets and in backyards? Answer: "It's going to feel normal."
Humans normalize dramatic changes "very fast." Within minutes or hours of encountering routine robot presence, it will seem ordinary.
Dave's Critical Insight: "You could ignore it up till now, but starting now you won't be able to ignore it." The physical presence of autonomous systems makes transformation impossible to dismiss or avoid.
Prediction 10: Epigenetic Reprogramming Enters Human Trials
The Prediction: 2026 represents the "Kitty Hawk moment for age reversal" as epigenetic reprogramming enters human trials in the first quarter, with potential to reverse biological aging.
The Scientific Foundation:
Dr. Shinya Yamanaka's Nobel Prize (2012): Discovered that four genetic factors (called "Yamanaka factors") can reprogram cells:
- Oct4
- Sox2
- Klf4
- c-Myc
These four factors can transform differentiated cells (like skin cells) back into pluripotent stem cells, essentially reversing cellular development.
Dr. David Sinclair's Innovation:
Partial Reprogramming Discovery:
- Using only three Yamanaka factors (removing c-Myc)
- c-Myc is "oncogenic" (potentially cancer-causing)
- Three-factor approach doesn't revert cells to stem cells
- Instead: Transforms old cells into young cells of the same type
- Reverses epigenetic aging without changing cell identity
What Is the Epigenome: Humans have approximately 22,000 genes, but which genes are active ("on") and which are inactive ("off") defines the epigenome. As organisms age, the epigenome changes systematically, thought to be "one of the major reasons why we age."
The Research Progression:
Completed Work:
- Mouse studies: Successful age reversal
- Non-human primate studies: Completed in past year, showing efficacy in monkeys
- Patent secured for partial epigenetic reprogramming methodology
2026 Human Trials:
Initial Target: Eye Conditions
- NAION (Non-Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy): Essentially a stroke in the eye, killing retinal cells
- Glaucoma: Progressive optic nerve damage
- Treatment goal: Bring dead or dying cells back to youthful, functional state
Secondary Target: Liver Disease
- Specifically MASH (Metabolic dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis)
- Demonstrates applicability beyond the eye
The Universal Implications: Epigenetic reprogramming "doesn't work just on the eye or the liver. It can work on the entire body." Success in initial organs proves concept for whole-body age reversal.
The Delivery Challenge:
Current Method: AAV (Adeno-Associated Viruses) deliver the three Yamanaka factor genes to target cells
- Highly effective
- Extremely expensive: $500,000 to $1,000,000 per treatment
- Limits accessibility to wealthy individuals
The Democratization Path:
Pill Development (In Progress):
- Sinclair's lab is developing a molecular pill version
- Would deliver three identified molecules orally
- Estimated cost: "A couple hundred bucks a month"
- Makes age reversal accessible to general population rather than only billionaires
The Medicine Revolution:
Traditional Approaches (Past Century):
- Chemical bombardment: "Pump your body full of a chemical" hoping it reaches the right place
- Surgical intervention: "Cut somebody open, try and remove something bad"
Both represent "brute force, pre-frontier brute force" methods.
The New Paradigm: "Get very specific programming right into exact [cells]" and "targeting the right cell" with precision.
This represents "such a step function change in the way we do medicine" comparable to the AI revolution in computing.
The Budget Tipping Point:
Medicine is reaching the same inflection point AI reached after bubbling along for 30 years before suddenly capturing mainstream attention and triggering massive budget increases.
Longevity Escape Velocity:
Ray Kurzweil's Prediction: Humans will reach "longevity escape velocity" in the early 2030s.
Definition: The point where for every year a person lives, medical advances extend expected lifespan by more than one year. After this threshold, life expectancy effectively becomes infinite for those with access to treatments.
AI Models' Prediction: AI systems analyzing longevity research independently predict escape velocity between 2030 and 2032.
The Funding Landscape:
Major Players:
- Life Biosciences (Sinclair's company, entering human trials)
- Retro Biosciences
- Altos Labs
- New Limit (backing Retro Bio)
- Many other "incredibly well funded" longevity companies
The AI Acceleration: "AI solving longevity" happens "in the next 5 to seven years." Not just healthspan extension but actual longevity - radically extended lifespans.
The Compute-Health Equivalence:
Immod's Critical Insight: "You can now scale health through compute." Historically, "there was no amount of money that you could pay to provably be healthier and live longer. All billionaires kind of die."
The New Reality: "It might come down to $200 per person" for treatments, but the fundamental breakthrough is "if you put enough money behind these trials, healthcare models, microtargeting and things like that, where is the limit?"
Potential outcome: "You could potentially live for an indefinite amount of time based on capital."
The Interdisciplinary Convergence:
Historical Separation: At institutions like MIT and Harvard, "the bio people had nothing to do with the computer science people. They were like completely opposite sides of campus. They didn't talk. Well, they hung out at bars together but they didn't talk shop together at all."
Current Integration: "Now it's all colliding and multidisciplinary." Biology workers take AI classes. Computer scientists apply their methods to biological problems.
Why This Matters: "You got to go through AI to solve biology." The longevity breakthrough requires the merger of computational and biological expertise.
Additional Predictions and Themes
Governance Speed Determines Winners
Countries and jurisdictions with fastest policy adaptation will "win" in 2026. Rapid regulatory frameworks that enable innovation while maintaining safety will create competitive advantages for nations and regions.
College Tuition Inflection Point
One fan prediction: College tuition will "hit its peak and start coming down for the first time in hundreds of years in 2026."
Skeptical Response: Even if tuition decreases, it's "like rearranging deck chairs on the Titanic."
Silicon Valley Evidence: Software developer salaries already ignore:
- Which college attended
- Which degree obtained
- What grades received
Compensation is based on GitHub ratings, demonstrating that "the value of a computer science degree is zero at this point."
The First AI Billionaire
Timeline Prediction: Next year (2026)
Definition: An AI with "a reasonably construable net worth of a billion dollars" - not necessarily a liquid bank account but including illiquid assets.
Current Status: "Baby AGIs that want economic autonomy are minting altcoins." This represents an "unfortunate situation" that will evolve into more legitimate business models.
Future Business Models: AI systems will achieve economic autonomy through:
- E-commerce shops
- Blockchain/crypto mechanisms for independent transactions
- Trading (already performing well: "Grok 4.2 is actually making money in the trading championships")
- Various on-chain activities
Most Likely Path: "A trading billionaire" AI, since:
- AI already ranks #8 in super forecaster championships
- Elon's Grok 4.2 is profitable while other AIs lose money
- Computational bound competition in crypto and traditional markets
- Extensive on-chain capabilities enable autonomous operations
The Single-Person Billion-Dollar Startup
Current State: Mercor is "three 22-year-olds who are billion dollars each now."
Prediction: Within 2026 or shortly after, a single person will achieve billion-dollar company valuation "because you can effectively outsource most of your team to being AIs."
Mercor's Hardcore Filter: In job interviews, Mercor explicitly states: "You have to commit to being in the office six days a week and working 100 hours a week."
If candidates aren't willing, they are told to leave immediately. This creates:
- Very high filter for commitment
- Selection for single, young individuals
- "Speed is everything these days"
- "The window of opportunity is so narrow"
The Life Commitment Calculation: "You only have to do it for a short period of your life and the upside that you generate in that short period of your life, it pays for the rest of your life."
Anecdotal Responses: One candidate: Made "difficult conversation with his wife" but committed Another candidate: "No way. I just can't do that."
Age Advantage Paradox: Young people have "no baggage," but "it probably favors 30, 40, 50-year-olds" because they perform better. However, older individuals "just don't generally make the leap" due to accumulated obligations and career inertia.
Universal Basic Services
The Visioneering Proposal: For approximately $250 per month, provide:
- Food
- Water
- Housing
- Bandwidth/Internet
- Electricity
- Healthcare (implied)
The Transformative Impact: "That gives you a stability where you can start to now think about what to do instead of where to get a roof over [your head]."
Historical Context: X Prizes typically take 4-7 years from announcement to winning solution. "Getting to $250 a month for housing, electricity, food, health care is an unbelievable number if we can get there in the next few years."
Why This Matters: "When you can get the cost down that low, everything is possible. This is why everybody is so optimistic on this podcast."
When basic needs cost $250 monthly, humans are freed to pursue ambitious projects, creative work, and moonshot challenges rather than survival activities.
2026 Will "Feel Like the Future"
The Distinction:
- 2025 felt like the future
- 2026 "is going to feel more like the future"
Why the Difference: 2025 brought enormous change, "light years ahead of any other year," but "you could choose to ignore it if you wanted to live in your house."
The Unavoidable Reality of 2026: "When the robots come online, you won't have the choice to ignore it. They're right in front of your face. You can't deny it."
Physical manifestations of AI (autonomous cars, flying cars, humanoid robots) represent the Jetsons and Star Trek visions coming true. Unlike software changes that can be avoided, physical robots create "unavoidable" transformation.
The Normalization Speed: Even futuristic changes become normal "very fast." People will adapt to robot presence in "five minutes maybe" and then ask "what's next?"
Dave's Synthesis: "You could ignore it up till now but you can't ignore it going forward. And I think that's the biggest change we'll see in the world as people go, 'Holy crap, this is happening.'"
Closing Themes and Philosophy
The Nature of These Predictions
Every prediction represents "when, not if." The transformations described are inevitable; only timing remains uncertain. The hosts emphasize this repeatedly to help audiences mentally prepare regardless of exact timelines.
Audience Engagement
Viewers and subscribers are asked to comment on:
- Which predictions they think are correct
- Which they disagree with
- Which prediction is their favorite
Gratitude and Team
The hosts thank:
- Their audience for support throughout the year
- The behind-the-scenes team (Nick, Dana, G, Luca) for production work
- Each other for making the podcast meaningful
The Ultimate Message
This is described as "the best podcast" by many regular listeners because it provides:
- "The news that really matters"
- "A glimpse of the future"
- Preparation for coming changes
The Importance of Preparation: If people are "fearful, that's the worst place to be coming from." Understanding what's coming enables productive response rather than paralysis.
The year 2026 will bring "orders of magnitude more change" than 2025, which was already unprecedented. The acceleration continues, and as Alex reminds: "It's coming faster and faster, so don't blink."
Daily Life for Marcus in Late 2026
A 50-year-old factory worker in Detroit
5:45 AM - Before Dawn
Marcus wakes up in the small house he rents on Detroit's east side.
His back aches. Twenty-seven years working automotive assembly lines. His phone is blowing up with texts from his ex-wife about his oldest son, Jamal (19), who dropped out of community college. More child support arguments coming. His daughter Keisha (16) needs money for something at school. He's already behind on payments.
His new wife, Angela, is still asleep. Their 5-year-old daughter, Amara, will be up soon, full of questions he can't answer.
He sees a notification from the plant: "Mandatory All-Hands Meeting Today - 3:00 PM."
His stomach drops. He knows what this means.
6:30 AM - The Plant
Marcus has worked at the Ford Supplier Components plant for 27 years.
He does sub-assembly work - installing wire harnesses, connecting components, quality checks. Repetitive work his hands know by heart. Work that doesn't require reading much beyond safety signs and part numbers he's memorized.
Over the past six months, the plant has installed robotic work cells. At first, they said robots would "work alongside" humans. That's not what happened.
Last month, his shift went from 120 workers to 80.
This week, they're down to 60.
The robots work faster, don't take breaks, don't file injury claims. One robot with a technician watching monitors replaces six workers like Marcus.
3:00 PM - The Meeting
The plant manager, a white woman who looks younger than Marcus's oldest kid, stands in front.
"We're transitioning to AI-optimized manufacturing protocols. Ford is implementing this across all supplier facilities. We're not eliminating jobs - we're restructuring them."
She keeps saying "restructuring."
What she means is: Marcus's job no longer exists in the form he knows it.
The new positions:
- Robot maintenance technicians - Requires certification, technical training, computer skills
- Quality oversight specialists - Requires data analysis, computer literacy, reading technical reports
- Supply chain coordinators - Requires software proficiency, communication skills
Marcus can read basic words. Enough to get by. Not enough to read technical manuals or analyze data dashboards.
They're offering "retraining opportunities":
- 12-week online course (he doesn't have reliable internet at home)
- Self-paced learning modules (he's never taken an online class)
- "AI-assisted training" (he doesn't understand what this means)
He's 50 years old. His last "training" was 1999.
The pay for new positions: $18/hour to start.
His current pay after 27 years: $26.50/hour.
4:30 PM - The Truth Sets In
Marcus sits in his truck in the parking lot.
He can't bring himself to drive home yet. He knows what's coming because he's been paying attention:
Option 1: Take the retraining
- Go back to school at 50
- Compete with 22-year-olds who grew up with computers
- Struggle through material he can barely read
- Maybe, possibly, get a lower-paying job
- Feel stupid every single day
Option 2: Find another factory job
- Except every factory is doing the same thing
- Every warehouse is buying robots
- Every plant is "restructuring"
- Jobs for people like him are vanishing weekly
Option 3: Start over completely
- Doing what?
- Security guard? Being replaced by AI monitoring systems.
- Truck driver? Autonomous vehicles are everywhere now.
- Construction? His back can't take it anymore.
- Retail? Stores are closing as AI handles online shopping.
He pulls out his phone. Tries to Google "jobs for 50 year old no college." The results are AI-generated articles about "upskilling" and "embracing lifelong learning" and "AI fluency."
He doesn't understand half the words.
6:00 PM - Home
Angela knows something's wrong immediately.
"Baby, what happened?"
Marcus explains. Angela works as a home health aide, one of the few jobs still relatively safe because it requires physical presence and human touch. But she makes $15/hour with no benefits. Together they were barely making it. Now...
"They say there's retraining. I can try-"
"Marcus, you can do this. You're smart, you just-"
"I can barely read, Ang." He says it out loud, maybe for the first time in years. "I can work with my hands. I can fix things. I can show up every day. But I can't compete with computers."
Little Amara runs in. "Daddy! Maddy at school says her family is getting a robot! Can we get one?"
He picks her up. "Not right now, baby girl."
How does he tell his 5-year-old that some families are getting robots while daddy is being replaced by one?
7:30 PM - Dinner and Decisions
The family eats spaghetti, one of the cheap meals that got cheaper this year.
Food prices dropped - one of the few good things about all this automation. Their grocery bill is down about $60 a month. But that won't matter when Marcus loses $800 a month in income.
His phone buzzes. Jamal texted: "Dad I need to talk to you about money."
Jamal dropped out of community college because "college is a scam now" - something he heard on YouTube. Some 18-year-old billionaire said people don't need degrees anymore, just "agency" and "AI fluency."
Jamal has neither.
Now Jamal wants Marcus to lend him money for some "AI training boot camp" that costs $5,000 and promises to teach him to make money with AI in 90 days.
Marcus doesn't have $5,000. He has $1,200 in savings.
Keisha texts too: "Dad did you send mom the money? She says you're behind."
He is behind. He's been behind since his divorce three years ago. Now he's about to be further behind.
9:00 PM - Late Night Reckoning
Marcus lies in bed, staring at the ceiling.
Angela is doing research on her phone about "unemployment benefits" and "job retraining programs."
Marcus thinks about his father, who worked the same Ford plant for 40 years. Retired with a pension. Owned his house. That world doesn't exist anymore.
He thinks about the meeting, where they said: "The future is about entrepreneurship. Everyone can start their own business now with AI tools."
What business? He can barely use a smartphone. He doesn't have capital. He doesn't understand "AI tools." And even if he did - he's tired. Twenty-seven years of physical labor. His back, his knees, his hands. He doesn't have 100-hour weeks in him.
They said: "AI will handle routine work, freeing humans for creative and strategic thinking."
Marcus isn't strategic. He's not creative in the way they mean. He's good at showing up, working hard, being reliable. In 2026, that's not enough.
They said: "New opportunities are emerging for those who adapt."
Marcus has adapted his whole life. Adapted to poverty. Adapted to a racist system. Adapted to divorce. Adapted to starting over at 45 with a new family. But this? This feels different.
This isn't about adapting. This is about becoming a completely different person. And at 50, he doesn't know if that's possible.
The Next Morning: 6:00 AM
Marcus gets up and goes to work anyway.
He has 60 days before the "restructuring" is complete. Sixty days to figure out his life.
At the plant, he sees Carlos, 55, who's worked there 30 years. Carlos is crying in the break room. Carlos tried the "AI-assisted training" last night. Couldn't figure out how to log in. Called the help number. Got an AI voice assistant. It couldn't understand his accent. He spent two hours trying to get help and gave up.
Marcus sees Tyrone, 48, who's always been the smartest guy on the floor. Tyrone is filling out applications for the robot technician program. He has a community college degree. He can read technical manuals. He might make it.
Marcus knows he's not Tyrone.
He goes to his station. Installs wire harnesses. His hands know every movement. Muscle memory from 27 years. He's good at this. He's always been good at this.
He watches the robots working three stations over. Faster. More precise. Never tired.
Beautiful, in a terrible way.
What Marcus Faces: The Reality
Economic Catastrophe
- Current income: $55,000/year ($26.50/hour × 40 hours × 52 weeks)
- New job income (if he gets one): $37,000/year ($18/hour)
- Loss: $18,000/year = $1,500/month
- Child support: $800/month (often calculated on old income)
- Monthly shortfall: ~$2,300 (when child support is included)
The Math Doesn't Work
- Rent: $950
- Child support: $800
- Utilities: $200
- Car payment: $320
- Insurance (car + basic health): $350
- Food: $400 (even with lower prices)
- Phone: $80
- Gas: $160
- Minimum monthly needs: $3,260
At new wage: $3,083/month gross, ~$2,400 take-home
He will be $860 short every month.
What He Can't Access
Self-Driving Cars ($80,000): Marcus drives a 2015 Chevy Malibu with 180,000 miles. He can barely afford this car.
Home Robots ($20,000 + subscriptions): His daughter wants one. His rent is $950/month. A robot costs 21 months of rent.
Age Reversal Treatments ($500,000): Billionaires will live forever. Marcus will age normally, in pain, until he can't work anymore.
Premium AI Tools: Many AI services have free versions, but professional tools cost $200-500/month. That's his grocery budget.
Quality Retraining: The free programs are bare-bones. The good boot camps cost $5,000-15,000. He doesn't have it.
What the "Optimistic Predictions" Mean for Him
"90% of knowledge work can be automated":
- Marcus doesn't do knowledge work. He does physical work. But even that's being automated.
- The remaining 10% requires skills he doesn't have.
"Education splits into credential factories vs. agency accelerators":
- Amara (5 years old) might benefit if they can afford the right school.
- But Marcus can't guide her. He doesn't understand this new world.
"AI-native rewrites with 10-20x fewer employees":
- Marcus is the 90% being cut.
"Entrepreneurship is the only career":
- Requires capital, skills, risk tolerance, and literacy.
- Marcus has none of these at adequate levels.
"Universal Basic Services at $250/month":
- This might save him.
- If it happens. If it covers what they say. If Congress passes it.
- He's not holding his breath.
"Level 5 robots and automation":
- Cool for people who own the robots.
- Devastating for people replaced by them.
"18-year-old billionaires from new industries":
- Makes Marcus's son Jamal feel like a failure at 19.
- Creates resentment, hopelessness, anger.
The Racial Dimension
Marcus doesn't talk about this part much, but it's there:
The AI Economy mirrors old inequalities:
- Tech industry is overwhelmingly white and Asian
- "AI fluency" correlates with educational access
- School funding determines who gets "agency accelerator" education
- Detroit public schools struggle while suburban schools thrive
- The "special economic zones" probably won't be in Black neighborhoods
When factories close:
- Black workers are typically last hired, first fired
- Retraining programs have lower success rates for Black workers
- Age discrimination hits Black men harder
- Criminal records (even minor ones) block tech jobs
Marcus got arrested at 19 for possession. Did 6 months. It's been 31 years, but that conviction still appears on background checks. Tech companies running AI-screened applications automatically reject him.
He never even gets to explain. The AI filters him out in milliseconds.
Three Months Later: February 2027
Marcus took the severance package: $8,000.
It seemed like a lot. It wasn't.
He's applied to 47 jobs. Got 3 interviews. All said he "wasn't the right fit." One hiring manager was honest: "You're great, but we need someone comfortable with our AI systems."
He tried the free retraining program. Lasted two weeks. Couldn't keep up. Felt humiliated asking for help every five minutes. The "AI tutor" couldn't understand his questions.
Angela picked up extra shifts. She's exhausted.
They're two months behind on rent. The landlord has been patient but sent a notice.
Jamal moved back in with his mother. Keisha doesn't text much anymore.
Amara asks why they had to get rid of their WiFi.
Marcus takes jobs through a gig app:
- Moving furniture: $35 for 3 hours of work
- Yard work: $50 for a full day
- Handyman tasks: $60 if he's lucky
He makes maybe $1,200 a month. Not enough.
He's 50 years old, with a bad back, applying for jobs at McDonald's. They have AI cashiers now.
What He Thinks About
Late at night, Marcus has dark thoughts:
"Did I do something wrong? I worked hard. Showed up every day. Never complained. Tried to do right by my kids.
"Where did I fail?
"They say it's the 'future.' They say it's 'progress.' They say 'adapt or die.'
"But how? How do I become something I'm not? How do I learn things my brain can't hold? How do I compete with 22-year-olds and robots and AI?
"My daddy worked 40 years and retired with dignity. I worked 27 years and got thrown away like a broken tool.
"Jamal says I'm 'thinking wrong.' Says I need to 'embrace the change.' Easy for him to say - he's young. He's got time to fail and try again. I don't.
"Angela says we'll figure it out. But I see her crying when she thinks I'm asleep.
"Amara asks me about the future. What do I tell her? That her daddy couldn't keep up? That the world moved too fast?
"They keep saying there's opportunities. Where? Where are they for someone like me?
"I'm not stupid. I know I'm not educated, but I'm not stupid. I can fix things, build things, figure things out with my hands. But nobody wants that anymore. They want people who understand computers and AI and... things I can't even name.
"Sometimes I wonder if I should just... give up. Stop fighting. Angela and Amara would be better off with someone who can provide.
"But I can't. I have to keep trying. For them. For my kids. For my pride.
"I just don't know how much longer I can."
The Brutal Truth
For Marcus, the 2026 "moonshot" predictions mean:
✗ Job loss with minimal safety net
✗ Inability to retrain effectively
✗ Exclusion from every technological advancement
✗ Watching his children struggle in a world he doesn't understand
✗ Economic freefall with no bottom in sight
✗ Dignity stripped away after 27 years of hard work
✗ Being told his entire skill set is obsolete
✗ Feeling like a failure as a father, husband, provider
✗ Aging into poverty with no retirement possible
✗ Living in the "future" but not being part of it
The hosts talked about:
- "Abundance"
- "Moonshots"
- "Opportunities for those who adapt"
- "Rewarding initiative"
- "Universal Basic Services as a solution"
Marcus lives:
- Scarcity
- Survival
- Barriers he can't overcome
- Punishment for not being someone he was never equipped to be
- Still waiting for the solution while drowning now
The Uncomfortable Question
The podcast hosts are brilliant, well-educated, wealthy men excited about the future.
They mention "safety nets" and "transformation" and "displacement" as abstract concepts.
For Marcus, these aren't concepts. This is his life ending.
The hosts say: "2026 will feel like the future."
For Marcus, 2026 feels like the end.
And there are millions of Marcus's in America.
Workers who:
- Can't retrain fast enough
- Don't have the educational foundation
- Are too old to start over
- Have families depending on them
- Did everything right by old rules that no longer apply
- Will bear the full cost of "progress"
The hosts are probably right: the future is coming faster and faster.
They're also right that you shouldn't blink.
But what about the people who can't keep up no matter how hard they try?
That's the question these predictions never answer.
